What
are electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are waves that we
cannot see but are composed of electromagnetic energy. Since the forces of this
energy or electric and magnetic fields change both temporally and spatially,
they are known as waves.
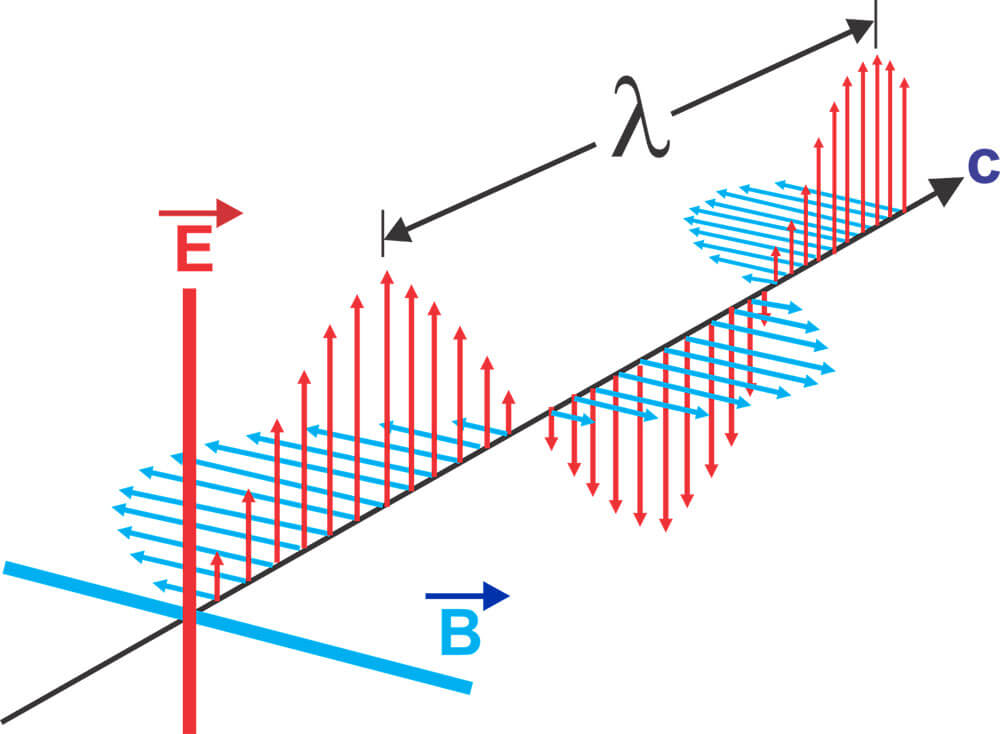
But how are
these electromagnetic waves formed? A dipole can be used to change the
direction of the current flow and the force. When the force on the dipole is at
its highest point, a magnetic field is created around it. This magnetic field
has the same direction as the current flow.
Within one
oscillation, the current flow drops completely to zero twice, which means that
the charge carriers within the dipole accumulate at the respective ends and the
electric field lines move from the positive to the negative end.
If the dipole is
reversed, the electric field weakens and the magnetic field increases. This
means that alternating magnetic and electrical vibrations are produced,
sometimes creating an alternating electromagnetic
field. In addition, this alternating electromagnetic field can even be
separated from its dipole, which means that it spreads at the speed of light. This
is where the electromagnetic wave appears.
There are
different types of electromagnetic waves: radio waves, microwaves, X-rays,
mobile phone radiation, even light. These can be described with characteristics
very similar to the waves in water as:
Of course, it is
also possible to calculate these waves mathematically. Maxwell's equations are used for this, which show us how the
varying electronic and magnetic fields are related to each other.
If you need more
information on this topic or have any questions, you can contact our
specialized staff at any time.