How long do magnets last?
Many factors can influence the time it takes to lose its magnetic properties. However, magnets maintain their magnetization for hundreds of years, for example, a permanent magnet, more specifically a samarium magnet, takes 700 years to lose half of its magnetic strength. If we go to neodymium and ferrite magnets, they have almost permanent magnetism.
The factors that affect the lifetime of a magnet are:
Temperature change: depending on the type of permanent magnet, we can use a magnet at one temperature or another, since a neodymium magnet and an alnico magnet are not the same.
The neodymium magnet has a working temperature of 80ºC to 200ºC, while the alnico magnet can withstand temperatures from -250ºC to 425ºC.
When choosing the permanent magnet we want to use, we will have to take into account the application we want to use it for. It is not the same to be used for holding it inside furnaces or in magnetic separators.
Contact with other magnetic elements: when storing a magnet we must take into account that there is some kind of magnetic insulator, such as a plastic separator. As we already know, plastic is one of the most known and used magnetic insulators nowadays; in this way, we will avoid that the presence of ferromagnetic elements that around do not damage the magnetization of the magnet.
In the same way, we have to take into account that there is no other type of permanent magnet nearby since the permanent magnet with greater magnetic strength takes away strength from the smaller one. Also keeping magnets with opposite charges nearby can affect and accelerate the loss of charge of the magnet.
Damage and physical shock: a magnet that has fallen to the ground or has been hit several times will have its magnetic power damaged. Depending on the magnet some have a higher resistance to corrosion than others, a clear example is the neodymium magnet that despite being the most powerful magnet has a lower tolerance to corrosion, so it is usually used with a nickel-plated coating, which serves as protection against scratches and external chemical agents.
To extend the life of the magnets we have to take into account these factors and treat the magnets correctly with the appropriate care.
What are ferromagnetic materials?
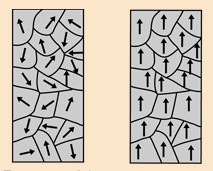
Ferromagnetic materials are substances that have a high magnetism in the same direction as the magnetic field because of it. This type of magnetism stands out for its high sensitivity to magnetic fields.
These materials are formed with metal ions which form domains. The domain is the space in which a uniform magnetization is found, in other words, when all the atoms are aligned and in the same direction.
Ferromagnetic materials have been in use since they were first used for navigation.
Ferromagnetic materials are used for various applications, some of the most commonly used are permanent magnets, transformer cores, magnetic tapes, and memory storage. They are also used for motors, sensors, and transformers.
Types of ferromagnetic materials
The primary characteristics that ferromagnetic materials must have are greater ease of magnetization and high permeability. In addition, if the magnetic field is suppressed, the magnetization will persist. The properties of ferromagnetic materials are several, but the most important are: their high magnetic induction and their simplicity of gathering the magnetic field lines, which subsequently descends to a large accumulation of flux density.
The most common ferromagnetic materials are:
Nickel: :
Nickel, as well as its alloys, has high durability and is a good conductor, together with cobalt, which is also very resistant to corrosion.
In addition to these, we can find Gadolinium, dysprosium, permalloy, awaruite, and wairakite.
The classification of ferromagnetic materials depends on the coercivity they possess, for instance. the intensity of the magnetic field they need to be demagnetized. Ferromagnetic materials can be soft or hard:
Soft ferromagnetic materials: they are easily magnetized and demagnetized. They also have the ability to increase magnetic induction. These materials are used in the construction of electrical machines, generators, and motors.
Hard ferromagnetic materials: once magnetized, they become permanent magnets, which have a high coercivity and are therefore often used as permanent magnets. These types of magnets are used for telephone rings and loudspeakers.
What are industrial magnets and what types are there?
Industrial magnets are very powerful magnets that are used in the industrial sector, as they are adaptable to all types of sectors and we can find them in any shape. These magnets are known for different types of industrial magnetic magnets such as magnetic resonance and motor activation. They are also known for their different qualities, grades and for preserving the properties of residual magnetism. Likewise, this type of magnet can be found in different magnetic materials, with different qualities against different external factors such as corrosion, ease of manufacturing, vibration, porosity, temperature to which it can be subjected to work.
What types are there?
Industrial magnets can be classified into permanent magnets and non-permanent magnets:
Non-permanent magnets are electromagnets that need an external electric current to become magnetized or demagnetized. To demagnetize, it is only necessary to deactivate the current of the magnetic core. These magnets have control of the force in the magnetic field, which has the ability to control the amount of electric current. Non-permanent magnets require a magnetic field which is generated through an electric current located inside a coil of wire and held by a core made of soft iron. We can find different types of electromagnets according to the property we need, for example:
- Rectangular electromagnets
Industrial permanent magnets can be made of ceramic, alnico and rare earths; they are made of a ferromagnetic material which is magnetized by an external magnetic field. This type of magnet is capable of being in a magnetized condition over an extended period of time. Permanent magnets maintain their state without external help, and are manifested with 2 poles and an increase in intensity near the poles of the magnetic field.
In permanent magnets we can find the following classification:
Within each type of magnet, there is a wide range of shapes, depending on the required need. We can find: blocks, discs, rings, rods, segments...