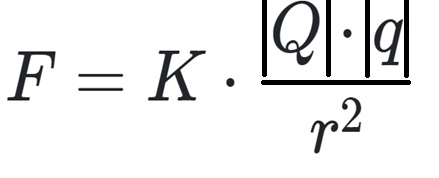
Coulomb’s law
Coulomb’s law was invented by Charles Coulomb; a French physicist who in 1785 did a paper at the Academy of Sciences in Paris. He was in charge of collecting various experiments on charged bodies. Through these experiments, he was able to obtain several results that together were what we know today as Coulomb’s law.
How is the force obtained by Coulomb’s law?
Coulomb’s law is the relationship found in the interactions (forces exerted by an electric field) between charges. Subsequently, the result of the charge according to the international system is symbolized by the letter Q and its unit of measurement is the same Coulomb (C).
To obtain the force using the law having two charges, we need to apply the following formula:
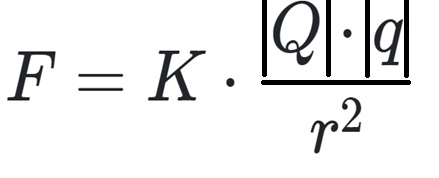
- F = Coulomb force
- |Q| = first point charge (C)
- |q| = second point charge (C)
- r = distance between two point charges (m à meters)
- kc = electrostatic constant, 8.988-10 9 ·C-2

In the case that Coulomb’s law has three charges, we find that these acquire a triangle shape. In the case of three forces, the method we will use to find the resultant force is the Parallelogram:
Fr2 = F21,2+F21,3+2F1,2F1,3cos∅
The magnitude of the electric forces that have the capacity of attraction and repulsion between charges is guided by the principle of electrostatics or the law discovered by Charles Coulomb. Since it is a vector quantity, its expression in vector form:
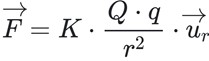
El vector de F= fuerza eléctricaem
El vector de ur=vector unitario
If the result of the force is positive, it is called a repulsive force, whereas if the result is negative, it is called an attractive force.
Coulomb’s law K depends on the medium and can be expressed by the dielectric constant or will allow the medium.
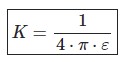
ε=ε0 à the vacuum permittivity (8.85 ·10 -12 C2 /N·m2)
In which applications can we find it?
This law can be found in several applications, for example:
- Electric motors
- Globe charged with electrostatic electricity
One application where Coulomb’s law is needed is in the study of crystalline structure. The ions in this crystalline structure are responsible for balancing the electrical forces. With the help of these forces, it is possible to make a simpler study of the crystalline structure that we need.