Lambert’s law
Lambert’s law or also known as beer lambert’s law establishes the empirical relationship connecting the absorption of light and the properties of a material as light travels.
This law was discovered in several different and independent ways, the first to discover it was the Frenchman Pierre Bouguer in 1729.
The beer-lambert law is composed of Beer’s law and Lambert’s law. Both laws are based on the behavior of radiation absorbed by a sample. The difference between these two laws is that Lambert’s law predicts the effect that the thickness of the medium creates, while Beer’s law implies the effect of concentration, both on the fraction of radiation which absorbs.
Lambert’s law says that the loss of the intensity at the moment it is in the medium is directly proportional to the intensity and the path length. In other words, if the intensity increases, the length increases and if the intensity decreases the length decreases with it.
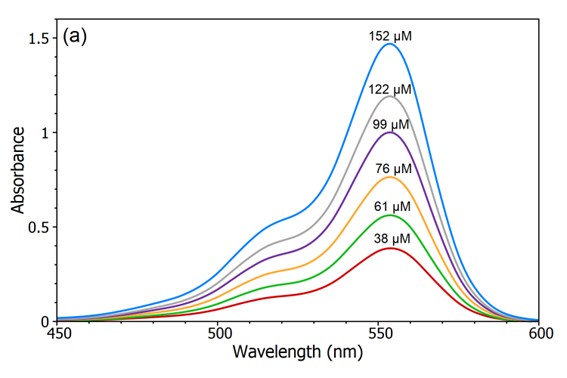
The Beer-Lambert law as its main utility is to know the determination of the concentrations of the solutions. Against it, it states that the total amount of light emanating from the sample can decrease due to the following three phenomena:
– Concentration is the number of materials absorbed at the moment of its trajectory.
– Optical path distance à the distance the light has to pass through the element.
– Absorbance à the probability of a photon being absorbed by the sample.
This law establishes the connection between the absorption in the radiation and the density of the sample.
What is the formula of Beer Lambert’s law?
The parameters taken into account in this law in addition to the material properties are:
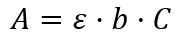
– A: absorbance of the solution at one wavelength
– ɛ: molar extinction coefficient (M-1 – cm-1 )
– b: cuvette pitch length (cm)
– C: concentration of the solution
What are transmittance and absorbance?
In this
law, we find two concepts: Absorbance and transmittance
– Absorbance is the amount of radiation absorbed by a material.
– Transmittance is the proportion of light that passes through a material in a given time.