What is the temperature coefficient?
The temperature coefficient symbolized as α is a property, which does not depend on the amount of substance or size, of materials that quantify the relationship between the alteration of this property of a material and the temperature range. This temperature coefficient is expressed in K (according to the International System of Units).
The constant α is obtained with the following formula:
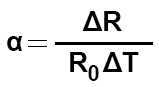
R0 = initial resistance
ΔT = temperature change
ΔR = change in resistance
The negative temperature coefficientof resistance is called NTC (Negative temperature coefficient), it is given to the reduction in resistance with an increase in temperature, this coefficient is usually found in non-metallic substances and semiconductors.
While the positive temperature coefficient of resistance is called PTC (Positive temperature coefficient), it occurs when the temperature increase increases the resistance value of a material. PTCs can be found in pure metals.
Below, we can see the table of coefficients of variation of resistance per degree Celsius of temperature.
Material α °C Material α °C Carbon 0.0005 Niccolite 0.0002 Nickel 0.0047 Copper 0.00382 Advance 0.00002 Kruppine 0.0007 Wolfram 0.0045 Tungsten 0.0041 Gold 0.0034 Lead 0.0037 Nichrome 0.00013 Platinum 0.0025 Aluminum 0.0039 Iron 0.0052 Manganite – Brass 0.002 Silver 0.0038 Mercury 0.00089 Tin 0.0042 Phosphor bronze 0.002
If the temperature changes and increases by 10°C, the rate of change of chemical or biological systems will vary; this can be found with the temperature coefficient Q10, which is needed in chemical reactions.
Temperature coefficient of resistance
Thetemperature coefficient of resistance is the measure of alteration that we find inthe electrical resistanceof some substances of the degree of temperature variation.
The resistance (R) for a temperature variation (∆t) in degrees Celsius is found due to:
R = R0 -(1+α – ∆T)R0 =reference resistance
α =temperature coefficient
The PT-100 sensor, which is a temperature sensor, is required to know the resistance performance at changing temperatures of the medium.
The temperature coefficient of the electrical resistance establishes the increase or decrease of the electrical resistance according to the change of temperature and the essence of the different materials. This coefficient is found thanks to the resistance formula that varies depending on the temperature variation.
On our website, we have different types of magnetic control equipment meet the needs of our customers.