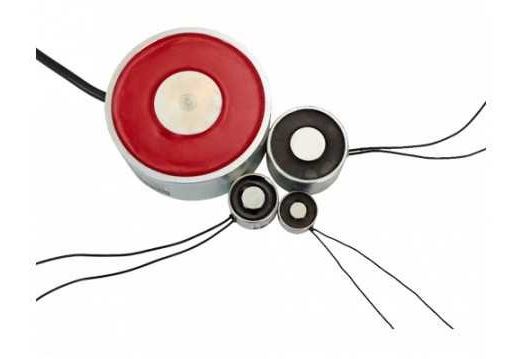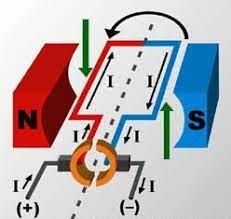
What is an electro-permanent magnet?
The first electro-permanent magnet was created in 1824 by the physicist William Sturgeon. This physicist connected a wire to the two ends of a battery, this wire was wound to an iron bar as we can see in the photo.
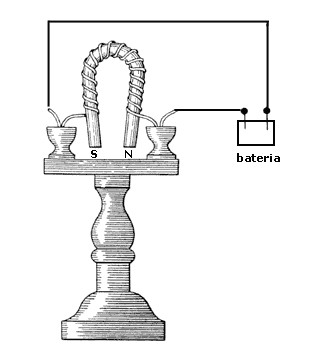
Later, the passage of time the electro-permanent magnet evolved into the magnet we know today.
What is an electro-permanent magnet?
An electro-permanent magnet or also known as direct current electromagnets are a type of magnet made of ferrous alloys that produce a constant field and intensity, in other words, the current is given due to the circulation of electrons moving from the pole (-) to the pole (+), these maintain the same polarity.
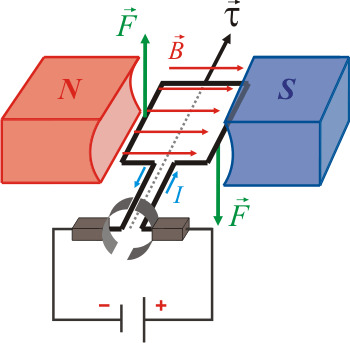
DC electromagnets are responsible for converting electric current into the mechanical current.
The electro-permanent magnet is used for the following characteristics:
As its name suggests, it has a direct current, i.e. it has an uninterruptible power supply.
It has a flat piece F1112 and a thickness of 3µ.
They have the capacity to maintain 35ºC of temperature.
The air gap between the center of the extractor and the rotor is zero.
If the magnet is a neodymium magnet, as this type of permanent magnet already has a high magnetic force, it does not require an electric current. However, in the case of an electric current, it will neutralize the force that the neodymium magnet already possesses from the beginning.

How does an electro-permanent magnet work?
The operation of the electromagnets of direct current is due to its 24V power supply, at the moment in which we activate the current, a magnetic field is produced, where it concentrates on an iron armature helping to fix any type of fastening.
Electromagnets are activated directly in contact with the metal part. This type of electromagnet is predestined to offer a permanent and comfortable operation.
Uses and applications of electro-permanent magnets
Applications that require a direct current to operate are televisions, computers, mobile phones….. On the other hand, like all electromagnets, they are used for electromagnetic brakes and clutches, as well as electric motors. DC electromagnets are used for applications that require manipulation of metal objects in industrial robotics, as they are required for positioning parts.