
Difference between axial, radial, and diametrical magnetization
Magnetization is the process by which magnets become magnetized and acquire the characteristic properties of magnetic elements. Due to this phenomenon, the object acquires the strength to attract or repel a metallic object. There are different types of magnetization of a magnet, depending on the line of induction, in other words, the way the magnetic field is represented.
Ferromagnetic materials can be magnetized by magnetic induction whereby magnetic fields produce electric fields. The induced magnetism is created by the strength of such a field.
Types of magnetization
The 3 types of magnetization that we can find depending on the different magnetizations are:
Axial: the axial magnetization type is characterized by having a magnetization that is from one side of the magnet to the other, in other words, the magnetic induction lines go from one pole to the other (from top to bottom).
Below, we can find several magnetizations with different numbers of poles that both have an axial magnetization.
| Representation | Number of poles |
 | Single pole |
 | Two poles |
 | Four poles |
 | Multiple poles |
 | Unipolar |
 | Four poles on one side |
 | Unipolar, single pole |
As we can see all poles have a horizontal magnetization.
Radial: radial magnetization is characterized as the magnetization of rings, discs, and cylinders. In addition, the representation of the magnetic field lines is found across the radius. This type of magnetization is found in the manufacture of motors, sensors, and actuators. Its orientation is multi-directional, i.e. it is found across the radius.
| Representation | Number of poles |
 | Single pole |
Diametral: material that has been diametrically magnetized has a magnetization that lies across the width of the magnet, i.e. across the diameter (from right to left). As we can see all poles have a vertical magnetization.
| Representation | Number of poles |
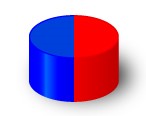 | Single pole |
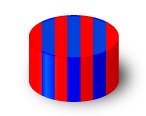 | Multiple poles |
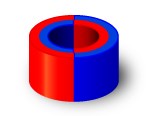 | Diameter and direction, one pole |
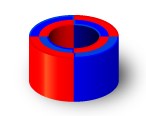 | Diameter and direction, four poles |
To know the magnetization process of a magnet, we must bring it close to some other metallic element.
The difference between axial and diametral magnetization lies in the magnetization force about the location of the magnetic field. Axial magnetization, having the direction of magnetization horizontally, the force will predominate on those faces. On the other hand, diametral magnetization is magnetized in its diameter. In addition to these two types, we find the radial magnetization which has multiple poles so it has a wider range of applications.